The Dow Jones Industrial Average, or Dow Jones for short, has been used as a means to measure the performance of the US economy for the last 128 years. Discover more about the Dow Jones in this article.
What is the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, otherwise known as DJIA, or DJ for short, is a stock index created by Wall Street Journal founder Charles Dow to measure the development of the US stock market. At 138 years old, it is also one of the world's oldest stock indexes.
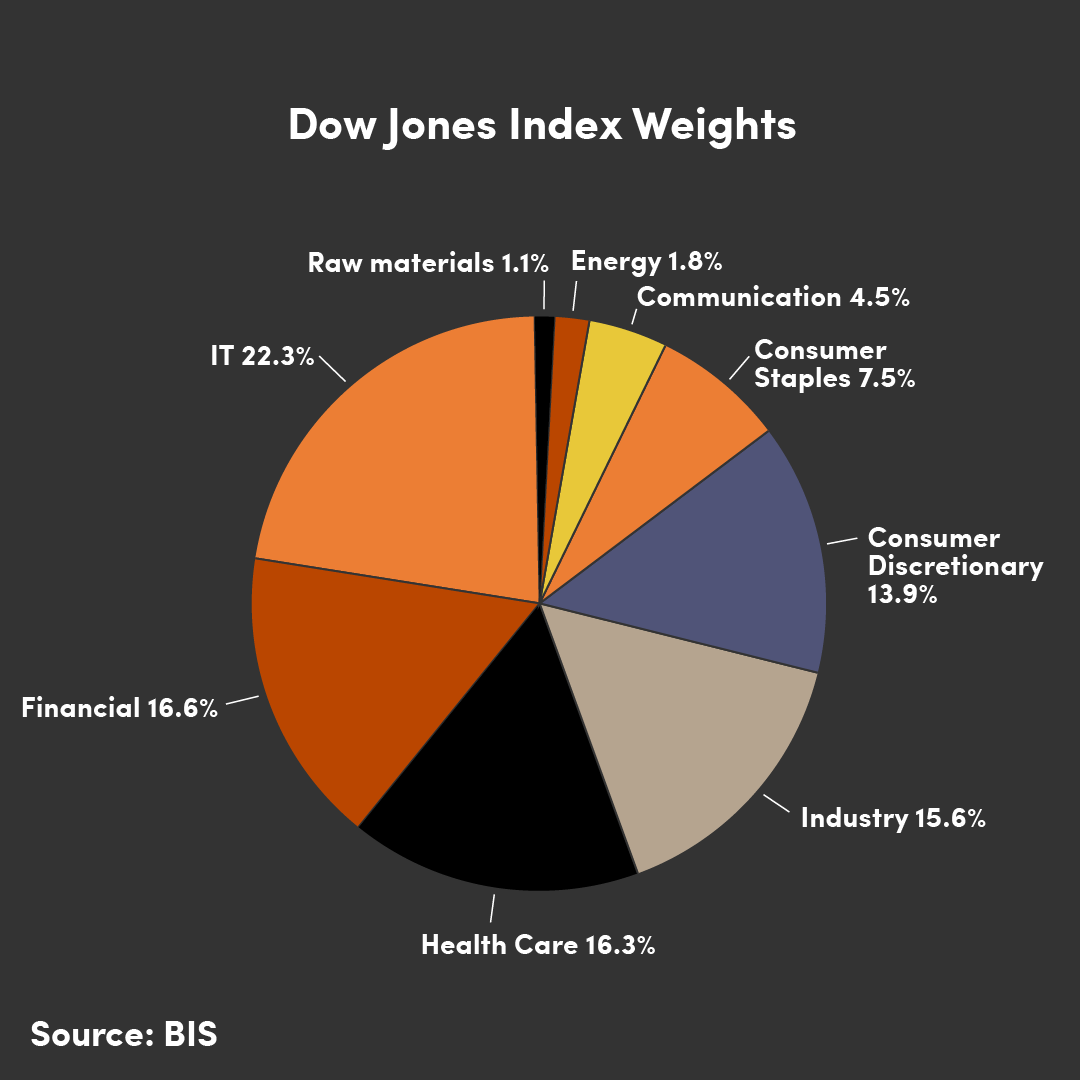
The Dow Jones consists of a total of 30 stocks, usually the largest or most well-known listed companies in the United States, covering a broad range of sectors, including industrial, financial, technology, retail, and insurance.
Due to the high correlation between its constituent stocks and the real economy, the performance of the Dow Jones is often considered a key metric in determining the health of the US economy.
How is the value of the Dow Jones calculated?
The Dow Jones is 'price-weighted', meaning the higher an individual constituent stock's price, the more influence it will have on the overall value of the index.
This method of calculation is different from that of the S&P 500 or Nasdaq-100, both of these examples being 'capitalization-weighted' instead.
Quick Summary:
- The DJIA was launched on the 16th of February 1885
- It has 30 constituent stocks, typical examples being UnitedHealth, Goldman Sachs, Home Depot, Microsoft, Salesforce, McDonald's
- Its value is determined by ‘price-weighted’ calculations
How are stocks selected for the DJ30?
As stocks that are selected for the Dow Jones need to be the 'most representative' within their respective industries, their performance is closely monitored. In some cases, this can mean removal from the Dow Jones index if seen to be 'under-performing'. For example, the original 12 stocks included in the Dow Jones at inception have all since been removed.
In the modern day and since 1928, the Dow Jones has included 30 stocks, with one constituent stock being removed and replaced every two years on average.
What’s so industrial about the Dow Jones?
Despite its full name being the 'Dow Jones Industrial Average', the index no longer focuses on stocks purely of an 'industrial' classification.
In the modern day, the Dow Jones has expanded to include sectors such as technology, finance, and retail, to name some examples.
In any case, the word 'industrial' only has historical significance today.
What are some disadvantages of the Dow Jones?
- Its' method of value calculation means that stocks of a higher price may disproportionately affect index value
Owing to the 'price-weighted' algorithms by which the value of the Dow Jones is determined, companies with the same market capitalization but trading at different stock prices will have varying levels of influence on the overall value of the index. As price alone is not an accurate indication of true market value, this can mean the performance of the Dow Jones is not fully representative of real market conditions. - There are too few stocks within the Dow Jones
When compared to other major US stock indexes, like the S&P 500, the Dow Jones includes far fewer stocks. By virtue of this, it can be argued that the DJIA is not as representative of real market conditions as other indexes.
How can you trade the Dow Jones?#
One method to trade the Dow Jones index is by using contracts for difference, or CFDs, which, through the use of leverage, allow investors to trade with a small amount of funding. If price is expected to rise, traders can take a long CFD position and a short CFD position if price is expected to fall, making CFDs a good option for both long and short trading.
In addition, CFDs also have the welcome benefit of being tradeable 24 hours a day, meaning investors are able to react to after-hours events, such as earnings reports and market-moving news headlines, which would not be possible with other forms of investment due to market closure.
When trading CFDs, selecting the right CFD broker is essential. Here are three guidelines that you should bear in mind:
- Select reputable brokers to avoid disputes
- Select reliable brokers supervised by major global regulators to ensure you are protected
- Select a company that protects your funds and offers easy deposits and withdrawals
With over 25 years of history, OANDA is the world's leading CFD broker and offers CFD trading on the Dow Jones
OANDA holds six regulatory licenses worldwide:
- UK Financial Conduct Authority
- US Commodity Futures Trading Commission
- Canadian Investment Industry Regulatory Organization
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission
- Japan Financial Services Agency
- Monetary Authority of Singapore
What are the advantages to opening an account with OANDA?
- OANDA offers unique indicators and Expert Advisors (EAs)
OANDA offers dozens of unique technical indicators and EAs for beginners and professional traders. The OANDA Japan team develops these indicators and EAs, available to investors in Japan, Taiwan, and around the globe. - OANDA offers over 60 CFDs
OANDA offers quotes for CFDs on indices, currency pairs, commodities, and precious metals. Our spreads average 0.5 – 0.8 on the S&P 500, 2.7 – 3.2 on the Nasdaq, and 3.0 – 3.5 on the Dow Jones. We also offer very competitive spreads for other products. - Trade at home and on the go
You can trade with MetaTrader 4 or MetaTrader 5 for desktop or via the MT5 mobile app on your phone or tablet.